1. Which two layers of the OSI model have the same functions as the TCP/IP model Network Access Layer? (Choose two.)
Network
Transport
Physical**
Data Link**
Session
2. What is a primary function of the trailer information added by the data link layer encapsulation?
supports error detection**
ensures ordered arrival of data
provides delivery to correct destination
identifies the devices on the local network
assists intermediary devices with processing and path selection
3. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer?
No address is added.
The logical address is added.
The physical address is added.**
The process port number is added.
4. What device is considered an intermediary device?
file server
IP phone
laptop
printer
switch**
5. Which layer encapsulates the segment into packets?
physical
data link
network**
transport
6. Which statements correctly identify the role of intermediary devices in the network? (Choose three.)
determine pathways for data**
initiate data communications
retime and retransmit data signals**
originate the flow of data
manage data flows**
final termination point for data flow
7. What can be identified by examining the network layer header?
the destination device on the local media
the path to use to reach the destination host**
the bits that will be transferred over the media
the source application or process creating the data
8. What is the proper order of the layers of the OSI model from the highest layer to the lowest layer?
physical, network, application, data link, presentation, session, transport
application, physical, session, transport, network, data link, presentation
application, presentation, physical, session, data link, transport, network
application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, physical**
presentation, data link, session, transport, network, physical, application
9.
Refer to the exhibit. Which three labels correctly identify the network types for the network segments that are shown? (Choose three.)
Network A -- WAN
Network B -- WAN**
Network C -- LAN**
Network B -- MAN
Network C -- WAN
Network A -- LAN**
10. What are the key functions of encapsulation? (Choose three.)
allows modification of the original data before transmission
identifies pieces of data as part of the same communication**
enables consistent network paths for communication
ensures that data pieces can be directed to the correct receiving end device**
enables the reassembly of complete messages**
tracks delay between end devices
11.
Refer to the exhibit. Which networking term describes the data interleaving process represented in the graphic?
piping
PDU
streaming
multiplexing**
encapsulation
12. What is a PDU?
corruption of a frame during transmission
data reassembled at the destination
retransmitted packets due to lost communication
a layer specific encapsulation**
13.
Refer to the exhibit. "Cell A" at IP address 10.0.0.34 has established an IP session with "IP Phone 1" at IP address 172.16.1.103. Based upon the graphic, which device type best describes the function of wireless device "Cell A?"
the destination device
an end device**
an intermediate device
a media device
14.
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only end devices?
A, C, D
B, E, G, H
C, D, G, H, I, J
D, E, F, H, I, J
E, F, H, I, J**
15.
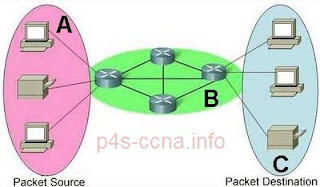
Refer to the exhibit. Which term correctly identifies the device type that is included in the green area?
source
end
transfer
**intermediary
16. Which three statements best describe a Local Area Network (LAN)? (Choose three.)
A LAN is usually in a single geographical area.**
The network is administered by a single organization.**
The connection between segments in the LAN is usually through a leased connection.
The security and access control of the network are controlled by a service provider.
A LAN provides network services and access to applications for users within a common** organization.
Each end of the network is generally connected to a Telecommunication Service Provider (TSP).
17.
Refer to the exhibit. What type of network is shown?
WAN
MAN
**LAN
WLAN
18. What is the purpose of the TCP/IP Network Access layer?
path determination and packet switching
data representation, encoding, and control
reliability, flow control, and error detection
**detailing the components that make up the physical link and how to access it
the division of segments into packets
19. Which characteristic correctly refers to end devices in a network?
manage data flows
**originate data flow
retime and retransmit data signals
determine pathways for data
20. What is the primary purpose of Layer 4 port assignment?
to identify devices on the local media
to identify the hops between source and destination
to identify to the intermediary devices the best path through the network
to identify the source and destination end devices that are communicating
**to identify the processes or services that are communicating within the end devices
21. Select the statements that are correct concerning network protocols. (Choose three.)
define the structure of layer specific PDU's**
dictate how to accomplish layer functions
**outline the functions necessary for communications between layers
limit hardware compatibility
**require layer dependent encapsulations
eliminate standardization among vendogrs
Network
Transport
Physical**
Data Link**
Session
2. What is a primary function of the trailer information added by the data link layer encapsulation?
supports error detection**
ensures ordered arrival of data
provides delivery to correct destination
identifies the devices on the local network
assists intermediary devices with processing and path selection
3. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer?
No address is added.
The logical address is added.
The physical address is added.**
The process port number is added.
4. What device is considered an intermediary device?
file server
IP phone
laptop
printer
switch**
5. Which layer encapsulates the segment into packets?
physical
data link
network**
transport
6. Which statements correctly identify the role of intermediary devices in the network? (Choose three.)
determine pathways for data**
initiate data communications
retime and retransmit data signals**
originate the flow of data
manage data flows**
final termination point for data flow
7. What can be identified by examining the network layer header?
the destination device on the local media
the path to use to reach the destination host**
the bits that will be transferred over the media
the source application or process creating the data
8. What is the proper order of the layers of the OSI model from the highest layer to the lowest layer?
physical, network, application, data link, presentation, session, transport
application, physical, session, transport, network, data link, presentation
application, presentation, physical, session, data link, transport, network
application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, physical**
presentation, data link, session, transport, network, physical, application
9.
Refer to the exhibit. Which three labels correctly identify the network types for the network segments that are shown? (Choose three.)
Network A -- WAN
Network B -- WAN**
Network C -- LAN**
Network B -- MAN
Network C -- WAN
Network A -- LAN**
10. What are the key functions of encapsulation? (Choose three.)
allows modification of the original data before transmission
identifies pieces of data as part of the same communication**
enables consistent network paths for communication
ensures that data pieces can be directed to the correct receiving end device**
enables the reassembly of complete messages**
tracks delay between end devices
11.
Refer to the exhibit. Which networking term describes the data interleaving process represented in the graphic?
piping
PDU
streaming
multiplexing**
encapsulation
12. What is a PDU?
corruption of a frame during transmission
data reassembled at the destination
retransmitted packets due to lost communication
a layer specific encapsulation**
13.
Refer to the exhibit. "Cell A" at IP address 10.0.0.34 has established an IP session with "IP Phone 1" at IP address 172.16.1.103. Based upon the graphic, which device type best describes the function of wireless device "Cell A?"
the destination device
an end device**
an intermediate device
a media device
14.
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only end devices?
A, C, D
B, E, G, H
C, D, G, H, I, J
D, E, F, H, I, J
E, F, H, I, J**
15.
Refer to the exhibit. Which term correctly identifies the device type that is included in the green area?
source
end
transfer
**intermediary
16. Which three statements best describe a Local Area Network (LAN)? (Choose three.)
A LAN is usually in a single geographical area.**
The network is administered by a single organization.**
The connection between segments in the LAN is usually through a leased connection.
The security and access control of the network are controlled by a service provider.
A LAN provides network services and access to applications for users within a common** organization.
Each end of the network is generally connected to a Telecommunication Service Provider (TSP).
17.
Refer to the exhibit. What type of network is shown?
WAN
MAN
**LAN
WLAN
18. What is the purpose of the TCP/IP Network Access layer?
path determination and packet switching
data representation, encoding, and control
reliability, flow control, and error detection
**detailing the components that make up the physical link and how to access it
the division of segments into packets
19. Which characteristic correctly refers to end devices in a network?
manage data flows
**originate data flow
retime and retransmit data signals
determine pathways for data
20. What is the primary purpose of Layer 4 port assignment?
to identify devices on the local media
to identify the hops between source and destination
to identify to the intermediary devices the best path through the network
to identify the source and destination end devices that are communicating
**to identify the processes or services that are communicating within the end devices
21. Select the statements that are correct concerning network protocols. (Choose three.)
define the structure of layer specific PDU's**
dictate how to accomplish layer functions
**outline the functions necessary for communications between layers
limit hardware compatibility
**require layer dependent encapsulations
eliminate standardization among vendogrs





Thanks
ReplyDeletethanks, good help
ReplyDelete